As a manufacturer of custom ceramics for thin-film circuit development for more than four decades, we are highly familiar with all the complexities involved in working with these materials to build a variety of circuits. Over the years, we’ve received quite a few questions about this technology, so we put together this Q&A to help answer some of the common questions you may have about thin film circuits.
Peter Matthews

Recent Posts
Examining the Definition of “Wideband” Through the Lens of Electronic Warfare Systems
In complex radio frequency (RF) applications, “wideband” has varying definitions depending on both the application of interest and the portion of the RF circuit you’re focused on. Wideband can be used to describe the entire spectrum shown in Figure 1 or large portions of it.
Powering Artificial Intelligence with Low-Loss Capacitors
In a short period of time, artificial intelligence (AI) large language models (LLMs) like ChatGTP and Claude have made leaps and bounds in terms of their size and sophistication. Size, as measured by the number of parameters, has increased by a factor of one thousand in merely five years, and it’s not projected to stop (Figure 1). This rapid growth raises numerous questions about the future of AI, while also presenting immediate challenges, with power consumption being a significant concern.
Topics: Capacitor
Exploring Our Energy Future with the Help of Capacitors
Companies across the world are engaged in fusion research; some are large national and international labs while others are start-ups looking for lower-cost alternatives to traditional fusion techniques. Their work is built on the premise that fused light nuclei have a net positive energy yield because their combined mass is less than the sum of their individual masses before fusion. Think Albert Einstein’s E = mc2.
Streamlining PCB Design with Crossovers for High-Frequency Applications
Considering the complexities of routing and signal integrity, it’s more and more common to see multilayer printed circuit board (PCB) designs where radio frequencies (RF) or digital traces cross on different layers of the stack. However, depending on the number of crossovers needed, the cost and complexity of this solution can outweigh the potential design benefits. For example, at high frequencies, multilayer designs are uniquely expensive to build; when laying out a ‘tile’ phased array, there’s very little space for components because of the λ/2 pitch of the array.
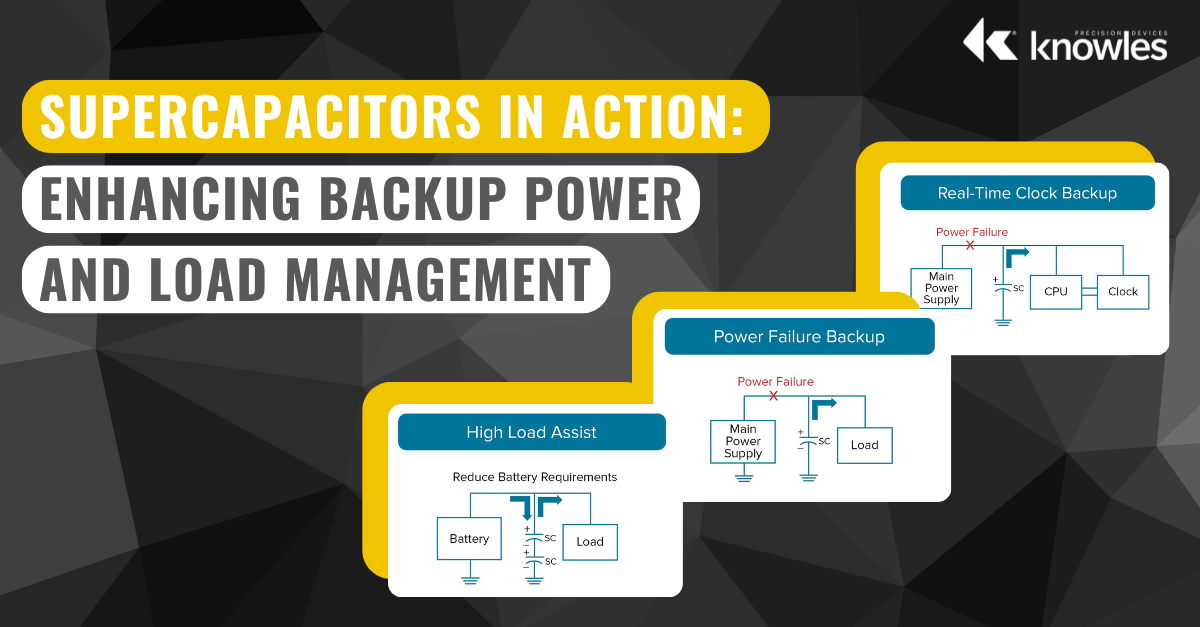
Supercapacitors in Action: Enhancing Backup Power and Load Management
Supercapacitors, also known as electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs), store energy electrostatically rather than via chemical reactions like traditional batteries. Their unique characteristics make them ideal for applications requiring short bursts of power and/or durability over time.
One of the fundamental roles of capacitors is charging and discharging energy predictably. Many electronics applications leverage capacitors to store energy and release it in a controlled pulse of current or voltage. Here, we’ll revisit how pulses are produced in a basic RLC circuit featuring a capacitor (C), inductor (L) and resistor (R).
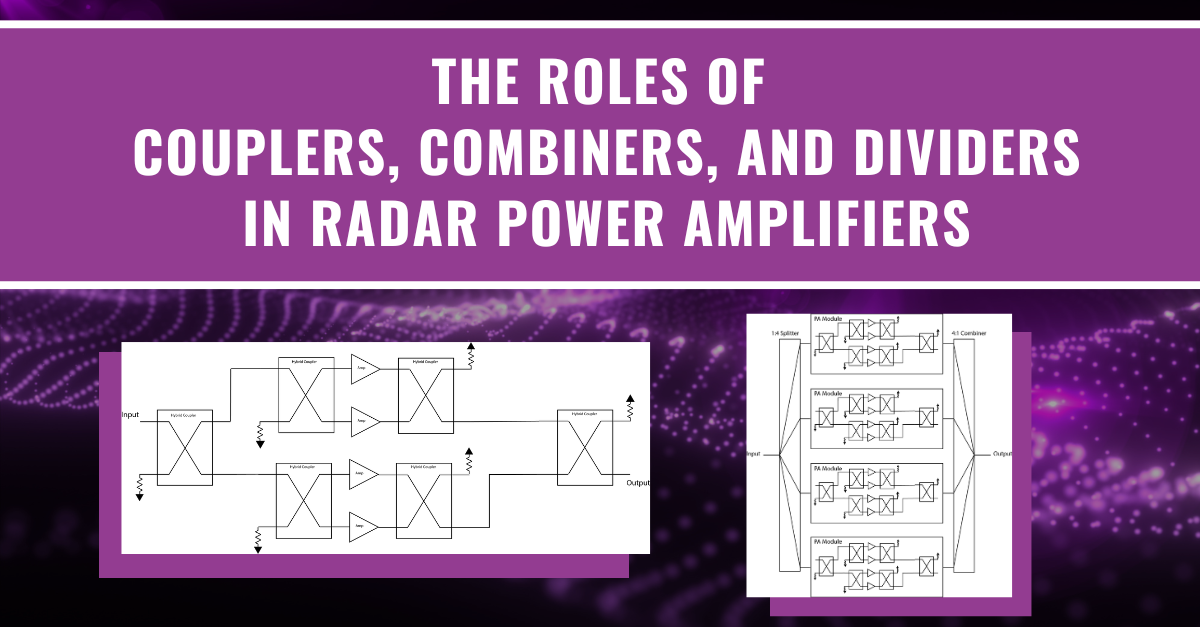
The Roles of Couplers, Combiners, and Dividers in Radar Power Amplifiers
At the most basic level, high-power amplifiers (HPAs) take signals from the waveform generator and increase the signal level to a higher power as shown in Figure 1. Depending on the system, the increase could take the signal from hundreds of watts to many megawatts. This is an essential step for many radar systems to boost the strength of a signal and improve range, resolution, and overall performance.
Supercapacitors vs. Batteries: A Comparison in Energy Storage Solutions
Supercapacitors feature unique characteristics that set them apart from traditional batteries in energy storage applications. Unlike batteries, which store energy through chemical reactions, supercapacitors store energy electrostatically, enabling rapid charge/discharge cycles. In certain applications, this gives them a significant advantage in terms of power density, lifespan, efficiency, operating temperature range and sustainability.
Topics: Capacitor
Enhancing Radar Performance: The Role of Gain Equalizers in RF Receivers
Low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) in radio frequency (RF) receivers are designed to amplify low-amplitude signals (i.e., less than -100 dBm) from an antenna without decreasing their signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In radar applications, a strong SNR increases the likelihood of detecting a target, so LNAs play an important functional role (Figure 1). Effective targeting requires both high resolution and high accuracy. A strong SNR translates to high accuracy.


.png)