High-speed broadband and fiber optic devices used across a variety of communication and military and aerospace applications require circuits that couple RF signals. Since this involves removing the DC component and allowing only the high-frequency AC component to pass or bypass, this can be a complicated process. The blocking capacitor needs to present a near reflectionless transition at the frequency the line is seeing and at a bandwidth that allows the entire signal to pass without degradation.
The Advantages of Knowles Precision Devices’ Broadband Capacitors
Topics: Capacitor
Capacitor Fundamentals: Part 5 – Dielectric Properties
Welcome to the Capacitor Fundamentals Series, where we teach you about the ins and outs of chips capacitors – their properties, product classifications, test standards, and use cases – in order to help you make informed decisions about the right capacitors for your specific applications. After describing dielectric polarization and losses in our previous article, let’s discuss five dielectric properties that affect capacitor performance.
Topics: Capacitor
Capacitor Fundamentals: Part 4 – Dielectric Polarization
Welcome to the Capacitor Fundamentals Series, where we teach you about the ins and outs of chips capacitors – their properties, product classifications, test standards, and use cases – in order to help you make informed decisions about the right capacitors for your specific applications. After describing factors that affect capacitance in our previous article, let’s discuss dielectric polarization and its relationship with frequency
Topics: Capacitor
Selecting Capacitors for High-Voltage X-Ray Power Supplies
As the backbone of the X-ray machine, X-ray tubes produce the radiation that generates the electromagnetic waves known as the “X-ray.” This is done by using a high voltage to accelerate the electrons released by a hot cathode to a high velocity. Those electrons then collide with the anode, which is a metal target usually made of tungsten. This process requires an input voltage typically ranging from 180 to 480 VAC with a power supply that transforms and steps up the voltage to extremely high voltage outputs ranging from 10kV and 120kV DC. A high-level diagram of the power supply required to power the X-ray tubes is shown in Figure 1.
Supporting Medical Advancement at Knowles Precision Devices
At Knowles Precision Devices (KPD), we handle the specialty components that go in the systems that can’t quit. We have the extensive resources and subject matter knowledge to innovate around the technical and environmental challenges facing high-impact industries including military, aerospace, and beyond.
Topics: Capacitor, News and Events, Medical, High Reliability
High-Performance Capacitors to Meet the Needs of Demanding Aerospace and Defense Applications
From military aircraft to electronic warfare defense systems, aerospace and defense applications are placing new demands on their power electronics. Defense electronics systems must function reliably for their lifetime while operating at higher voltages and wider temperature ranges, and all while becoming smaller, lighter, and consuming less power.
Topics: Capacitor, Military and Aerospace, High Reliability
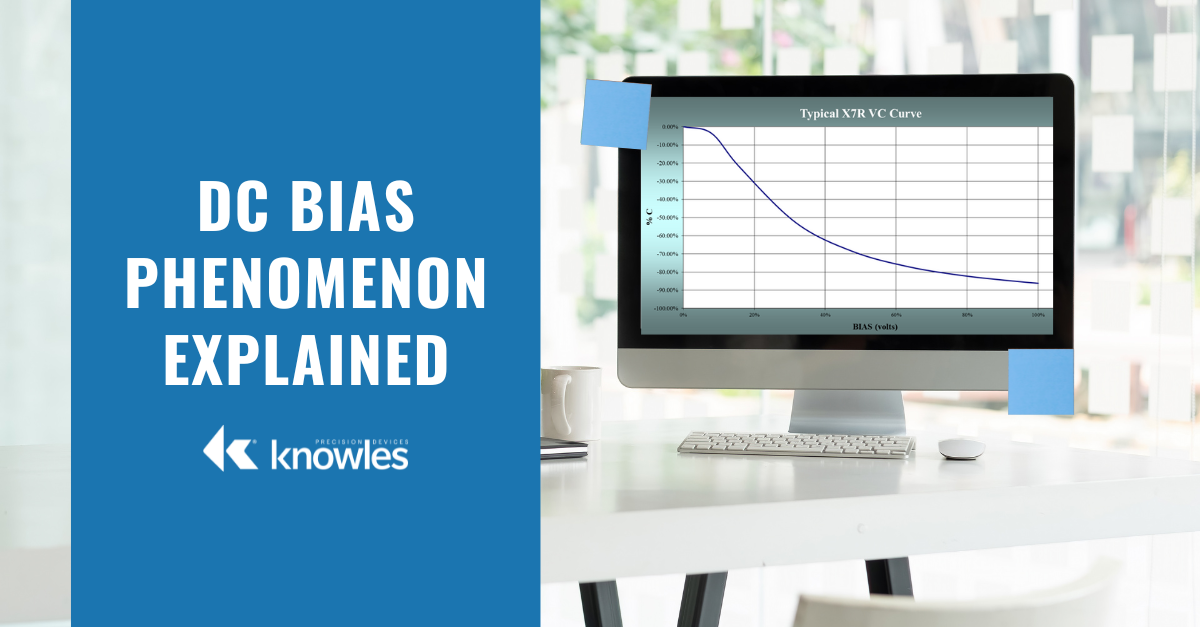
When constructing multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), there are two classes of dielectrics electrical engineers typically select from depending on the application – Class 1, which consists of non-ferroelectric materials such as C0G/NP0, and Class 2, which are ferroelectric materials such as X5R and X7R. One key difference between these materials comes in the form of capacitance stability as voltage and temperature increase. With Class 1 dielectrics, capacitance will remain stable when DC voltage is applied and operational temperature increases. On the other hand, Class 2 dielectrics, which have a higher dielectric constant (K), are less stable with regards to temperature, voltage, frequency, and time.
Topics: Capacitor
Capacitor Fundamentals: Part 3 – Factors Affecting Capacitance
Welcome to the Capacitor Fundamentals Series, where we teach you about the ins and outs of chips capacitors – their properties, product classifications, test standards, and use cases – in order to help you make informed decisions about the right capacitors for your specific applications. After describing common applications for capacitors in our previous article, let’s consider the factors and limitations that affect capacitance.
Topics: Capacitor
Capacitor Fundamentals: Part 2 – How are Capacitors Used?
Welcome to the Capacitor Fundamentals Series, where we teach you about the ins and outs of chips capacitors – their properties, product classifications, test standards, and common use cases – in order to help you make informed decisions about the right capacitors for your specific applications. After discussing capacitance and how capacitors work in our previous article, let’s talk about how capacitors are most frequently used in electronic circuits.
Topics: Capacitor
Welcome to the Capacitor Fundamentals Series, where we teach you about the ins and outs of chips capacitors – their nature and properties, dielectric behavior, product classifications, test and quality standards, and common use cases – in order to help you make informed decisions about the right capacitors for your specific applications. Part 1 discusses the key principles of capacitance and how a basic capacitor works.
Topics: Capacitor