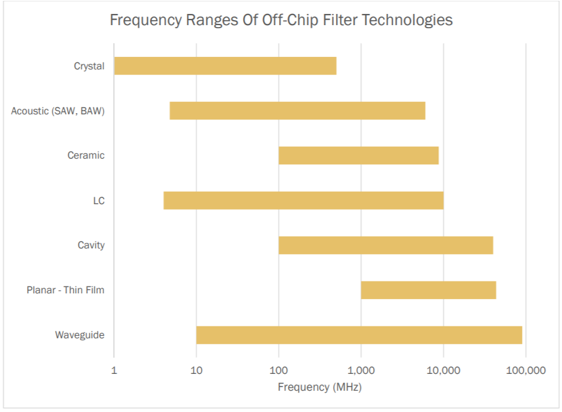
The millimeter wave (mmWave) part of the electromagnetic spectrum is at the high end of the microwave region, which spans ~300 MHz to 300 GHz, and is usually taken to mean frequencies from ~30 GHz to 300 GHz and wavelengths in the range of 1mm to 1cm (Table 1). This dramatically increases available bandwidth, thus expanding achievable data rates, which makes these frequencies extremely interesting to teams around the world working on fifth generation (5G) communications.
RF Filtering Techniques for Millimeter Wave Applications
Topics: 5G, RF and Microwave
Managing High-Temperature Electronics Environments Down to the Component Level
As complex electronic systems become more prevalent in our daily lives, the demand for high-temperature, high-reliability components continues to increase. Standard electronic components have an operating temperature of -55 °C to 125 °C, but the number of applications requiring functionality above 125 °C is growing. Components in these applications, like capacitors, must maintain their functionality and take the heat (literally and figuratively) while powered. To meet the brief, material and design of these high-temperature components must deviate from today’s standard.
Solving Tough Technical Challenges Through Agility and Experience
At Knowles Precision Devices, we thrive on working with companies who want to take technically challenging ideas and work through the details to figure out how to turn their seemingly impossible ideas into reality. This is because we are not limited to volume production and have extensive experience making specialty and custom parts. We are also familiar with the challenges associated with delivering high-reliability components as we supply many industries and applications that depend on the consistent functionality of custom-shaped parts. For example, we provide numerous space grade components and we are the only manufacturer who has developed planar array ceramic parts for the International Space Station.
Topics: Capacitor, Medical, High Reliability
Making a Reduced Form Factor, High-Performance Switch Filter Bank a Reality
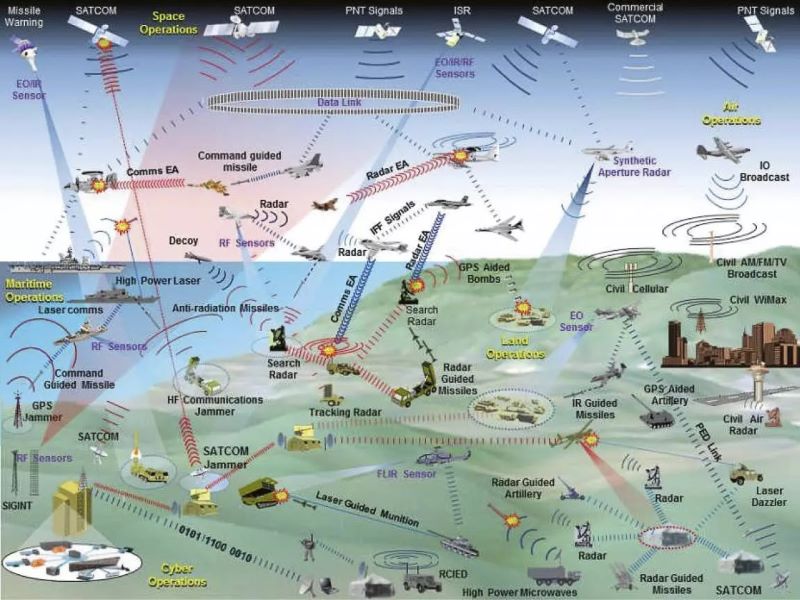
Many critical military operations around the world are increasingly relying on a variety of electronic warfare devices for a range of threat suppression, detection, and neutralization activities. This means that numerous devices operating across the RF spectrum including low-frequency devices in the VHF band and mmWave devices in the Ka band are necessary. As shown in Figure 1, when many electronic warfare devices are in use, a large number of signals are being sent and received and crossing paths. Therefore, it’s easy for any one of these devices to experience issues with interference if proper filtering techniques are not in place.
Topics: RF and Microwave, Military and Aerospace, Filtering
Knowles Acquires IMC to Expand Filtering Offering from the VHF to Ka Bands
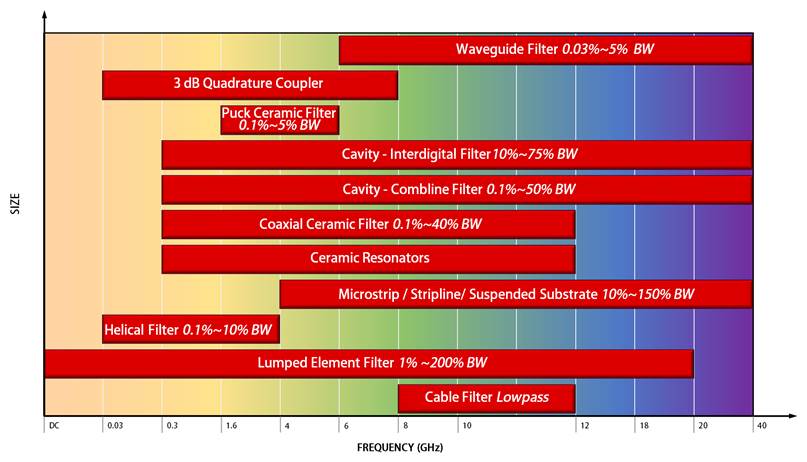
We are pleased to announce that the Knowles Corporation recently acquired Integrated Microwave Corporation (IMC), a leader in the design and manufacture of custom precision RF microwave filters and multiplexers for the aerospace, defense, and communications industries. With this acquisition, the Knowles Precision Devices Microwave group can now offer a complete range of RF and microwave filtering solutions that support applications from the VHF to the Ka band. In addition to the small, temperature-stable filters our customers have come to know us for, we can now deliver ceramic and cavity filters for lower frequency and/or higher power applications. The full range of the IMC filter technologies we now offer is shown in the graphic below.
Topics: News and Events, RF and Microwave
Build-to-Print Basics Part 15: Military and Space Grade Applications
To provide a better understanding of build-to-print in general and the breadth of our offerings, as well as how our thin-film technology can benefit your applications, we’ve put together a Build-to-Print Basics series. In this final post of our Build-to-Print Basics series, we discuss the quality standards we follow to ensure our components are qualified for military and space grade applications as well as the additional testing or spec design we can perform as needed by our customers.
Topics: Military and Aerospace, Build to Print
Fully Digital Beamforming – An Excellent Option for Emerging Military Applications
As early adopters of beamforming technology in the 1960s, aerospace and defense organizations have a lot of experience using the initial large-scale active electronically scanned arrays (AESAs) for military radar tracking applications. But these arrays aren’t as convenient for some applications today as the operational frequencies of the targets of interest for many military applications are increasing. This means the wavelengths of the signals that need to be monitored are getting shorter and these radar applications need denser arrays since antenna spacing needs to be set at one half the wavelength. For example, at 25GHz, the wavelength in free space is approximately 12mm (0.47”), leading to half-wave spacing for antennas of 6mm (0.24”). Also, as arrays become denser, the new challenge for RF system designers is avoiding interference in these tighter spaces, especially when transmitting signals.
Topics: Military and Aerospace, Filtering
To provide a better understanding of build-to-print in general and the breadth of our offerings, as well as how our thin-film technology can benefit your applications, we’ve put together a Build-to-Print Basics series. In part 14 we discuss a range of non-standard testing services our facilities can provide when needed by our build-to-print customers.
Topics: Build to Print
Webinar: Addressing Filtering Challenges in Digital Broadband Receivers for Electronic Warfare Applications
Today, electronic warfare applications need to detect a wide variety of signals ranging from UHF communications to GPS and other data signals in the L band to high-frequency radar signals that can fall in the X, S, or K bands. Therefore, these receivers need to operate across an extremely wide range of bandwidths to pick up and understand signals anywhere from 300MHz to 20GHz and beyond. However, a basic general wideband antenna isn’t sufficient for these applications because selectivity is needed to determine what you are actually listening to. Additionally, as if the task of designing an ultra-wideband receiver with selectivity wasn’t challenging enough, RF designers are simultaneously facing pressure to reduce the size, weight, and power (SWaP) of these applications as well.
Topics: RF and Microwave, Military and Aerospace, Filtering
Explosives are dangerous by design. For applications involving detonation, like munition and down-hole exploration, explosives should be built to avoid unintentional or premature detonation caused by any rise in temperature or shock. These applications require a number of specialty components including capacitors that discharge high energy at temperatures up to 200°C.
Topics: Military and Aerospace